Writing AT into the IEP
Where Should I Include AT Tools & Supports in the IEP?
Educational Accomodations and Supports
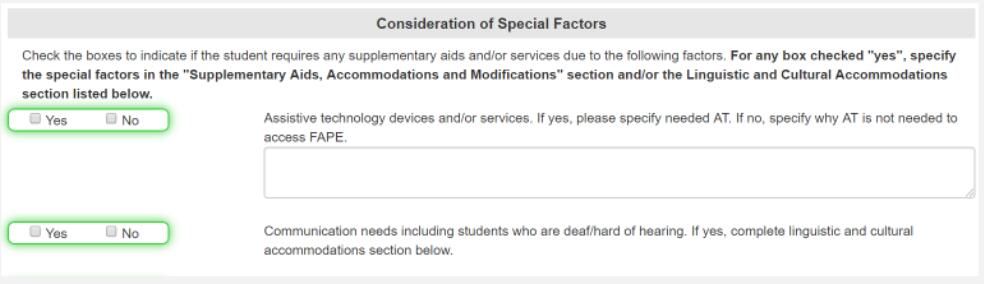
If you check NO:
Examples:
Student can complete the required instructional tasks and can access the school environment using standard classroom adaptations and the accommodations/modifications that are in place. Based on the student’s present levels of academic and functional performance, AT was considered and student does not need AT services to receive FAPE.
Assistive Technology has been considered and is not necessary at this time because the student is demonstrating expected progress on IEP.
If you check YES:
-
If the student is using multiple AT supports please specify the category (e.g. communicative, sensory, etc) and use the “general” purpose (e.g. to make expected process on their IEP Goals)
Example:
The student needs (communicative, sensory, academic, visual, mobility) assistive technology to make expected progress on their IEP Goals. See Supplementary Aids, Accomodations, & Modifications.
-
If student in AT trial (ADD in addition to statement above):
Example:
Educational team is considering additional assistive technology tools for (communication, alternative access, positioning, etc) and will amend the IEP to include those tools, as indicated.
-
If student only has ONE AT support state specific need and purpose in first box:
List general AT terms (no brand names)
Examples:
The student needs a voice output communication device in order to make expected progress on the IEP goal to use a variety of communicative functions.
The student needs accessible tools (e.g. adapted scissors) in order to make expected progress on the IEP Goal to participate in functional writing tasks.
1:1 tablet or computer device (such as a Chromebook) to support reading, writing, executive functioning, organization, sensory, vision, hearing, or access.
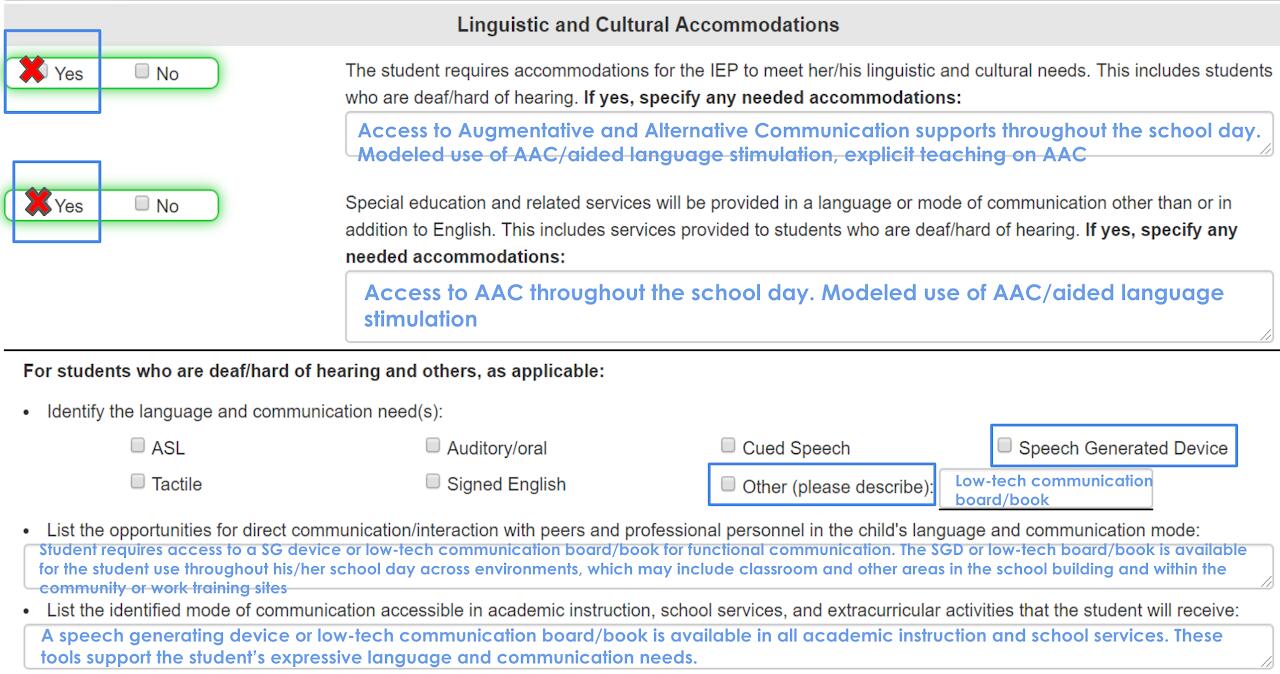
Select the second “yes” box for any student using dedicated OR non-dedicated AAC AND revised statement in the first box (except for District 25). See below for examples of what to state in Linguistic and Cultural Accommodations.
Linguistic and Cultural Accommodations
Supplemental Aids, Accodomodations, & Modifications
* List accommodation and WHY student needs accommodation!!*
Examples:
1:1 voice output communication system with a robust vocabulary (eg an iPad with TouchChat WordPower 42 Basic) in a Big Grip Case with a keyguard to communicate a variety of functions
Access to _______ voice output communication system (eg an iPad with TouchChat WordPower 42 Basic in a Big Grip Case with keyguard) to communicate a variety of functions.
1:1 tablet or computer device (such as an iPad or Chromebook) with appropriate apps or extensions (such as _______) to support reading, writing, executive functioning, organization, vision, hearing, sensory, or access.
Flexible Seating (e.g. hooki stool, move and sit cushion, ball chair, standing desk) to _______________.
Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance PLAAFPs
When documenting in the present levels of performance, include the assistive technology needs that are an integral part of the student’s access to the curriculum, taking into account the student’s strengths as well as weaknesses. Include the following:
- the generic/brand name of the AT tool
- function or purpose of the AT
Examples:
Student uses iPad with TouchChat WordPower 42 Basic in a HDE case with a keyguard, handle, and straps.
Student uses Co:Writer to support his/her ability to spell when completing written work.
Student uses Snap and Read to support his/her ability to access text.
Student uses an iPad with Go Talk Now Plus app, NSSEO 16 Scan vocabulary with two Jelly Bean Switches, a pillow speaker, switch/iPad Mounts, and a Tapio Switch Interface to communicate a variety of communicative functions in the classroom setting.
Goals and Objectives
When documenting in the goals page, include:
- the generic name of the AT feature (No brand names)
- AT does not have to be written within the goal for it to be needed to meet the goal.
Examples:
By the end of the one-year IEP period, given 2 models and 10 seconds of wait time, Susie will use her AAC system to describe a target item using an adjective and a noun 1 time per 15-minute classroom activity in 4/5 classroom opportunities.
By the end of the school year, Student will type a 5 sentence paragraph using word prediction software in a 15 minute time period and no more than 1 verbal prompt in 4/5 opportunities.
Additional/Meeting Notes
When documenting in the Additional Notes Page include:
- What AT options were considered
- The AT decision agreed upon by the team
- If there is any clarification needed about AT needs, uses, training, and/or implementation



